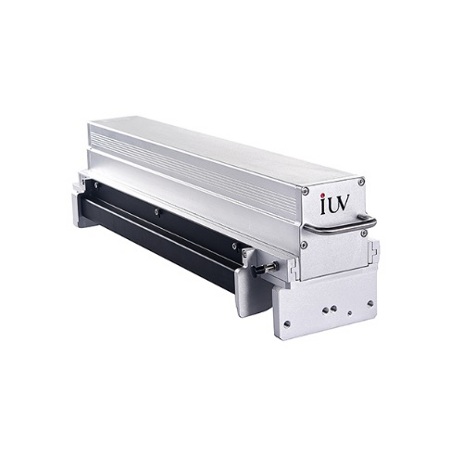
IUV’s UV LED curing system is made to more effectively and economically cure LED-formulated printing coatings and inks on web offset and sheetfed printing presses or bigger-format flexo presses and modern printing engines. It also has a self-developed water-cooling system and automatic width measurement system.
The lighting conditions are crucial for curing a UV ink, adhesive, or coating. It makes no difference if a microwave, an arc lamp, or a UV LED produces that light. For UV materials, adequate curing is ensured by exposure to the appropriate wavelength of light, at the proper intensity, for a long enough period.
Now let’s discuss some factors that might help you make the best decision of choosing a reliable UV LED Curing System:


Control Features
Certain UV systems have user-friendly controls that let you easily adjust the system’s power output, give feedback on the status of the power source and cooling system, and offer diagnostic data in the event of a malfunction. Some LED systems protect the array by keeping an eye on the coolant’s temperature and flow rate.
The “addressability” of modern LED control schemes allows you to individually switch on and off certain segments of the array to better fit components of varying sizes. When evaluating a source of light, you should also consider how well it will work with the rest of the curing line or machinery and whether or not it has the interface capabilities you require.
After-sale support
Planning for post-production support for the new UV LED curing method should begin at the feasibility stage. It is important to consider the services you’ll require when operations and production shift and to estimate how much time and money to modify the UV curing system to meet those needs.
Consider if you’ll need help with repairs, training for your employees, troubleshooting, spare parts on consignment, and so on. Ensure your partners can assist nationwide or internationally if you run several facilities.
Wavelength
To begin choosing a wavelength, it is necessary to identify the range of wavelengths to which the material being treated is most susceptible. Contact the manufacturer of the material or do experiments to determine the best option if you are unsure. In addition, consult our manual if you’re confused about the connection between wavelengths and cures.
Common curing wavelengths include 285 nm, 300 nm, 310 nm, 365 nm, 385 nm, 395 nm, and 405 nm. However, using the first three is rare because they’re in the UVB region, which provides less illumination (about 100 mW / cm2).
You can simultaneously release the light of many different wavelengths from UV lamps. If the exact wavelength that adds to the material curing isn’t known, don’t hesitate to contact experts, as UV LEDs can have their wavelengths blended to fit your needs.
Light Output Profile
Identifying the desired output profile for the specific use case is critical. In some cases, the light output might need to be smaller to prevent curing material on print heads, for instance. You can choose among a collimated beam, a divergent beam, or a wide-angle beam. More collimated alternatives may deliver lower dosages than wider orientations, although this could be a trade-off to evaluate.
Maintenance
If you’re in the market for a new UV light, consider how simple it’ll be to maintain and fix any potential problems. The reflector needs cleaning, but how? How soon can you get a new light bulb? How pricey are spare parts? You may swap out the modules for some arc lamps as fast and easily as a toner cartridge, whereas other designs need you to disassemble the system to do even the most basic maintenance.
It’s important to know if you can service the LED array of an LED source in the field or if you need to replace the whole thing when something goes wrong. For easier maintenance in the area, certain LED designs use plug-in modules. Basic cabling using several connectors and the least necessary moving components simplifies service. It’s convenient (and cheaper) to undertake basic upkeep without the help of an expert specialist.
Working Distance
Various factors, including the working distance needs of a given application, will affect the visual design of the lights. While most applications for UV LED curing systems only require a narrow focus range, curing items of varying sizes may necessitate a system with a significantly larger focus depth.
Take away
Users may easily incorporate the technology into any digital or analog printing machine, producing higher print quality at high production rates.
However, before considering a UV lamp for curing, you should study extensively. Choose your LED wisely for it to serve your needs. You can extend the lamp’s lifespan with careful and consistent upkeep. Remember that if you gaze at the light for too long, you could experience permanent eye damage.