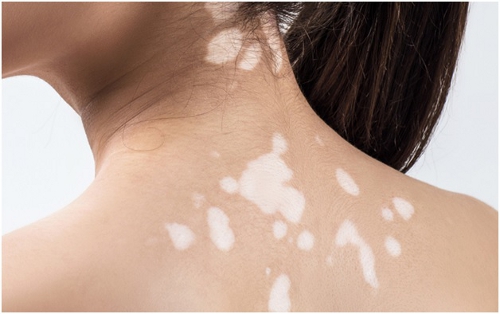
Vitiligo is a common pigmentation disorder in which the pigment-making cells (known as melanocytes) of skin are destroyed. Due to this, white patches appear on the skin. These white patches may occur on a particular section or all over the body. This disorder does not affect the physical health of the person, but the concern about the appearance may cause psychological, emotional, and social difficulties. Vitiligo can occur in any skin color, but it is more noticeable in people with darker skin.


Symptoms of Vitiligo:
The primary symptom of vitiligo is white patches in the skin. The discoloration usually shows on sun-exposed areas like face, arms, hands, feet, and lips.
Common symptoms of Vitiligo:
- Discoloration of the skin
- Premature graying or whitening of the hairs of your eyebrows, scalp, beard, or even eyelashes
- Discoloration in the inside tissues of mouth and nose
- Change in the color of the retina
- Discoloration in the mouth and nose
- The discoloration may also occur in armpits, genitals, navel, and groin
Vitiligo can begin at any age but most of the people get this pigmentation disorder in the teenage. Vitiligo is a non-contagious disorder.
Types of vitiligo:
1. Generalized Vitiligo: This is the most common type of disorder; the discoloration of the skin occurs in many parts of the body and often progress similarly on corresponding body parts.
2. Segmental Vitiligo: If the discoloration occurs in one side or a part of the body, then it is referred to as segmental vitiligo. The discoloration usually occurs at a younger age and stops after one or two years.
3. Localized Vitiligo: If the discoloration occurs in one or some parts of the body, then it is referred to as localized or focal vitiligo.
Sometimes the white patches formation stops without any kind of treatment. But for most of the cases, the discoloration spreads and involves most parts of the body.

Causes of Vitiligo:
1. Inheritance: About 20 percent of vitiligo patient has at least one or two relatives with the same disorder.
2. Genes: People with a certain type of genes makes them more susceptible to developing vitiligo. About 30 types of genes are identified which as associated with the skin condition, two of them are PTPN22 and NLRP1.
3. Environmental Triggers: Some environment triggers are also responsible for destroying melanocytes. Potential environmental triggers are sunburn, mechanical trauma, or exposure to some chemicals.
4. Autoimmune disease: People with some kind of autoimmune disease like Hashimoto’s disease or alopecia areata have a higher risk of developing vitiligo. About one in every four vitiligo patients has some kind of autoimmune disease.
Treatment and Prevention for Vitiligo:
• Sunscreen: Using sunscreen can be helpful because the lighter patches of skin are more sensitive towards the sun and can burn easily. Get advice from a dermatologist for your skin type.
• Phototherapy with UVB: This is the most common type of treatment for vitiligo. The combination of phototherapy with some other treatment has shown a positive effect on treating vitiligo. But the results of any kind of treatment are not fully predictable; there is still no full treatment of vitiligo.
• Skin camouflage: People with mild vitiligo can camouflage the white patches with cosmetic creams and makeup.
• Homeopathic remedies for Vitiligo: With the use of homeopathic remedies the early and milder cases of vitiligo can be treated with high chances of success. Contact Functional Medicine Doctors in NJ for the best treatment of vitiligo. These homeopathic remedies enhance the melanocyte formation. Common homeopathic remedies for vitiligo are:
- Silicea
- Kali Carbonicum
- Syphilinum
- Nitric Acid
- Arsenicum Sulfuratum Flavum
- Carcinosin
• Depigmenting: People with discoloration on most parts of the body, depigmenting can be an option. This process reduced the skin color in unaffected parts to match with the pale skin.
Skin graft and tattooing can be an alternative to hiding white patches.